Introducing the Traditional Chinese Medicine (Zhong Yi)
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is one of the great herbal systems of the world, dating back to the 3rdcentury BC. Yet throughout its history it has continually developed in response to changing clinical conditions, and has been sustained by research into every aspect of usage. This process continues today with the development of modern medical diagnostic techniques and knowledge.
Comparison between Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine
Firstly of all, traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine use different ways of organizing the information based on the same symptoms, same signs and same patient. For example, diagnosing the same patient with a lump in her breast, a Western doctor will see a cyst, lesion, fibroid or cancer whereas a Chinese medical doctor will see a stagnation of Qi, Blood, or Phlegm. The Western doctor will seek to prove the diagnosis with a biopsy of the hardened tissue. The practitioner of Chinese medicine will feel the unique quality of the pulse at the radial artery which may feel "wiry" or kind of hard, like a guitar string bouncing up and down beneath your fingers (as opposed to other pulses that can feel softer and more flowing), observe the color and shape of the tongue looking for purple in particular, with possibly a thick yellow coating. Also used for diagnostic purposes will be seemingly unrelated symptoms such as a sensation of constriction in the chest, abdominal bloating, heightened emotional sensitivity and a tendency to be easily angered and frequent headaches at the top or the sides of the head. This will allow the doctor of Chinese medicine to sum up with a diagnosis of "Qi, Blood or Phlegm stagnation."
Secondly, what Western medicine tends to diagnose and treat is the effect that the disease state has on the body itself. The Practitioner of Oriental medicine diagnoses and acts upon the energy that creates the disease state. In other words, some believe that the greatest strength of Western medicine is in its trauma care and therapies for acute problems, while Chinese medicine excels in the areas of chronic problems and preventive medicine. Focus of Chinese medicine that the scientific world is still struggling to accept is an internal substance that the Chinese call "Qi". In the West it could be described as bio-electric energy. Acupuncture seeks to treat health on the level of Qi. There are pathways in the human body wherein this Qi flows. Western medicine can see and measure certain changes in the body's chemistry and functional activities with these conditions, but cannot act upon these changes for lack of understanding of their cause. The symptoms are too divergent and unrelated from a materialistic standpoint. But when you factor in Qi energy and its properties, all these conditions make perfect sense.
Thirdly, another aspect of the difference between Chinese and Western medicine can be described as Chinese treats the Yang and Western treats the Yin. Everything in the universe can be described in terms of Yin or Yang. This is one of the underlying philosophies of Traditional Chinese Medicine. When applied to medicine in general, Western medicine acts upon the Yin of the body, the substance of the body, the actual cells and chemicals. Traditional medicine works more on the energy that animates those cells.
Last but not the least, the concept of "side effects" is not recognized as such in Chinese medicine while in Western medicine bases on chemical materials and its side effects are sometimes stronger than the therapeutic roles. The toxic effects of certain Chinese medicines is recognized according to degree, and if it is necessary to use a 'toxic' substance medicinally, it will be prepared in a special manner or combined with other medicines to reduce or eliminate toxicity if possible. Traditional Chinese medicine is based on natural plants and its comprehensive and flexible treatment strategies always bring about fantastic treatment result. So more and more people in the world are interested in traditional Chinese medicine, and it is becoming a major medical stream in the world.
Four Diagnostic Methods of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Bianque, who regarded as the god doctor in Chinese medicine, applied the comprehensive diagnostic techniques of traditional Chinese medicines, namely, the four diagnostic methods: observation, auscultation and olfaction, interrogation, and pulse-feeling and palpation. "Observation" means looking at the appearance and tongue fur. "Auscultation and olfaction" refers to listening to the sound of the patient's speech and breath. "Interrogation" refers to asking about the patient's symptoms and "pulse-feeling and palpation" is just in the literal meaning that feel the pulse by fingers' touch.
Popular and Useful Treatment of TCM
Moreover, Bianque's ways of treatment varied into more branches, such as acupuncture, moxibustion, herbal medicine, acupressure, cupping, therapeutic exercise and nutrition. Traditional Chinese medicine is a complete medical system that is capable of treating a very wide range of conditions.
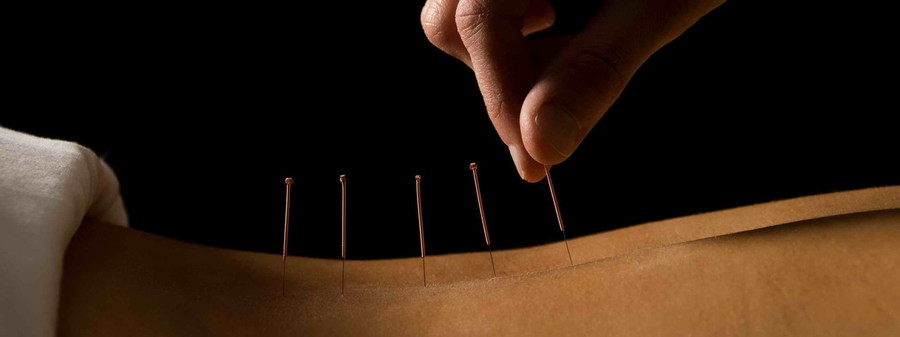
Acupuncture (Zhenjiu)
Acupuncture is practiced as medical treatments that are over 5,000 years old. Very basically, acupuncture is the insertion of very fine needles, (sometimes in conjunction with electrical stimulus), on the body's surface, in order to influence physiological functioning of the body. It can also be used in conjunction with heat produced by burning specific herbs, this is called Moxibustion. In addition, a non-invasive method of massage therapy, called Acupressure, can also be effective. Acupuncturists can use as many as nine types of Acupuncture needles, though only six are commonly used today. These needles vary in length, width of shaft, and shape of head. Today, most needles are disposable. They are used once and discarded in accordance with medical biohazard regulations and guidelines. There are a few different precise methods by which Acupuncturists insert needles. Points can be needled anywhere in the range of 15 degrees to 90 degrees relative to the skin surface, depending on the treatment called for.
Moxibustion (Aijiu)
Another popular treatment method is Moxibustion, which is the treatment of diseases by applying heat by burning specific herbs to Acupuncture points. Acupuncture and Moxibustion are considered complimentary forms of treatment, and are commonly used together. Moxibustion is used for ailments such as bronchial asthma, bronchitis, certain types of paralysis, and arthritic disorders.
Acupressure (Zhiya)
One of the most popular alternatives to Acupuncture is Acupressure. This is simply Acupuncture without needles. Stimulation of the Acupuncture points is performed with the fingers or an instrument with a hard ball shaped head. Another variation of Acupressure is Reflexology (also called Zone Therapy). This is where the soles of the feet and the posterior-inferior regions of the ankle joints are stimulated. Many diseases of the internal organs can be treated in this manner.
Cupping (Baguan)
Cupping is another type of treatment. This is a method of stimulating Acupuncture points by applying suction through a metal, wood or glass jar, in which a partial vacuum has been created. This technique produces blood congestion at the site, and therefore stimulates it. Cupping is used for low backache, sprains, soft tissue injuries, and helping relieve fluid from the lungs in chronic bronchitis.
Herbal Medicine and Modern Pharmacology
There is a growing body of research which indicates that traditional uses of plant remedies and known pharmacological activity of plant constituents often coincide. However, herbal medicine is distinct from medicine based on pharmaceutical drugs. Firstly, because of the complexity of plant materials, it is far more balanced than medicine based on isolated active ingredients and is far less likely to cause side-effects. Secondly, since herbs are typically prescribed in combination, the different components of a formulae balance each other. They undergo a mutual synergy which increases efficacy and enhances safety. Thirdly, herbal medicine seeks primarily to correct internal imbalances rather than to treat symptoms alone, Therapeutic intervention is designed to encourage a self-healing process. Chinese herbal medicines are very safe when prescribed correctly by a properly trained practitioner. Over thousands of years, experienced doctors have compiled detailed information about the pharmacopoeia and placed great emphasis on the protection of the patient. Allergic type reactions are rare, and will cause no lasting damage if treatment is stopped as soon as symptoms appear.
Functions of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Chinese medicine can be utilized to treat allergies, arthritis pain, and weight control, quitting smoking, back injury pain, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue and stress. Other illnesses and conditions that can be helped with Chinese medicine are digestive problems, menstrual problems, and urinary problems. Chinese doctors greatly emphasis on lifestyle management in order to prevent disease before it occurs. Chinese medicine recognizes that health is more than just the absence of disease and it has a unique capacity to maintain and enhance our capacity for well-being and happiness.